GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
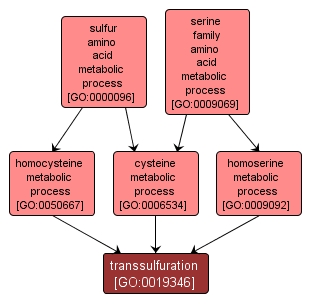
transsulfuration |
| Acc: |
GO:0019346 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The interconversion of homocysteine and cysteine via cystathionine. In contrast with enteric bacteria and mammals, Saccharomyces cerevisiae has two transsulfuration pathways employing two separate sets of enzymes. |
Synonyms:
- homocysteine-cysteine interconversion
- transsulphuration
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|