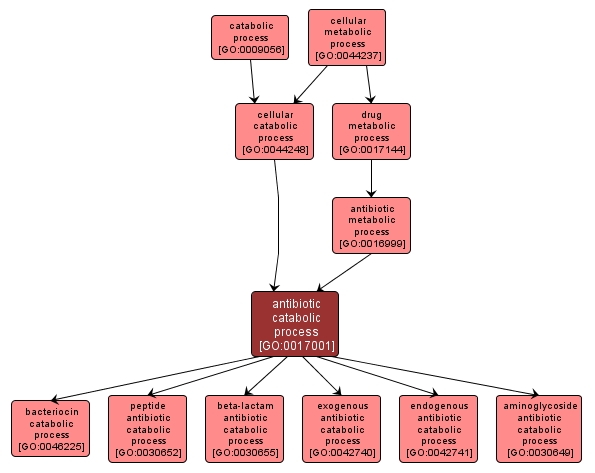
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
antibiotic catabolic process |
| Acc: |
GO:0017001 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of antibiotic, a substance produced by or derived from certain fungi, bacteria, and other organisms, that can destroy or inhibit the growth of other microorganisms. |
Synonyms:
- antibiotic catabolism
- antibiotic breakdown
- antibiotic degradation
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|