GO TERM SUMMARY
|
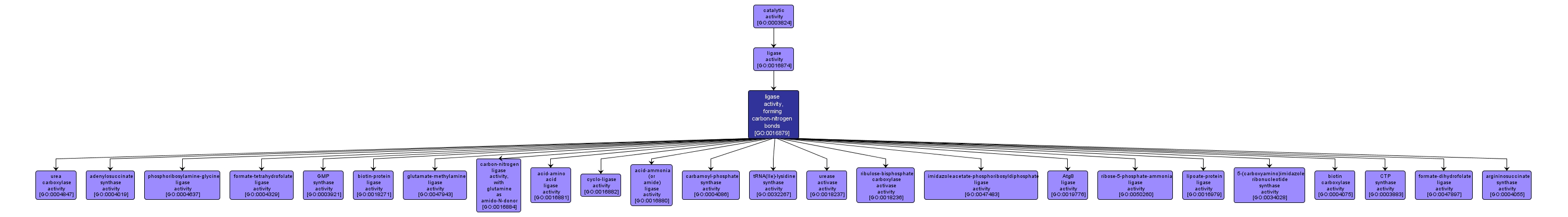
| Name: |
ligase activity, forming carbon-nitrogen bonds |
| Acc: |
GO:0016879 |
| Aspect: |
Molecular Function |
| Desc: |
Catalysis of the ligation of two substances via a carbon-nitrogen bond with concomitant breakage of a diphosphate linkage, usually in a nucleoside triphosphate. |
Synonyms:
- other carbon-nitrogen ligase activity
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|