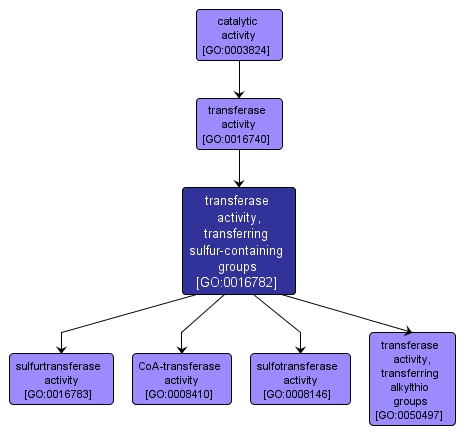
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
transferase activity, transferring sulfur-containing groups |
| Acc: |
GO:0016782 |
| Aspect: |
Molecular Function |
| Desc: |
Catalysis of the transfer of a sulfur-containing group from one compound (donor) to another (acceptor). |
Synonyms:
- transferase activity, transferring sulphur-containing groups
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|