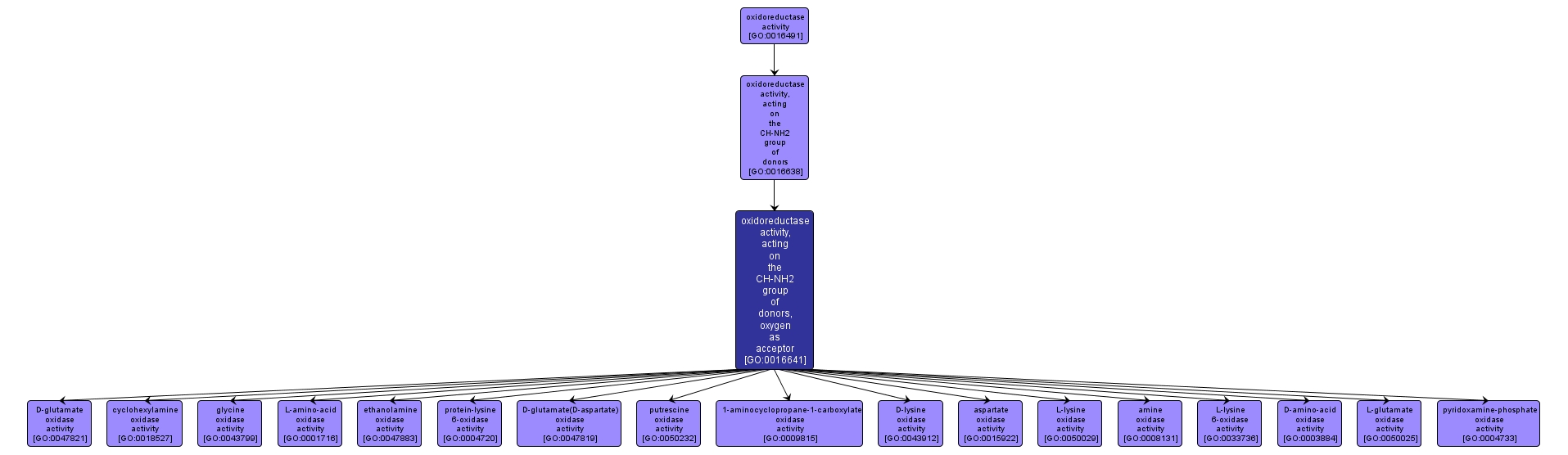
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
oxidoreductase activity, acting on the CH-NH2 group of donors, oxygen as acceptor |
| Acc: |
GO:0016641 |
| Aspect: |
Molecular Function |
| Desc: |
Catalysis of an oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction in which a CH-NH2 group acts as a hydrogen or electron donor and reduces an oxygen molecule. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|