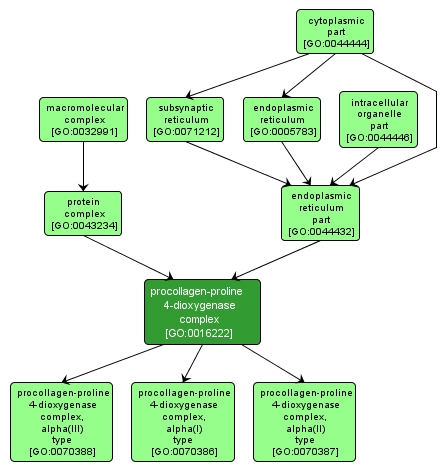
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
procollagen-proline 4-dioxygenase complex |
| Acc: |
GO:0016222 |
| Aspect: |
Cellular Component |
| Desc: |
A protein complex that catalyzes the formation of procollagen trans-4-hydroxy-L-proline and succinate from procollagen L-proline and 2-oxoglutarate, requiring Fe2+ and ascorbate. Contains two alpha subunits that contribute to most parts of the catalytic sites, and two beta subunits that are identical to protein-disulfide isomerase. |
Synonyms:
- prolyl 4-hydroxylase complex
- procollagen-proline, 2-oxoglutarate-4-dioxygenase complex
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|