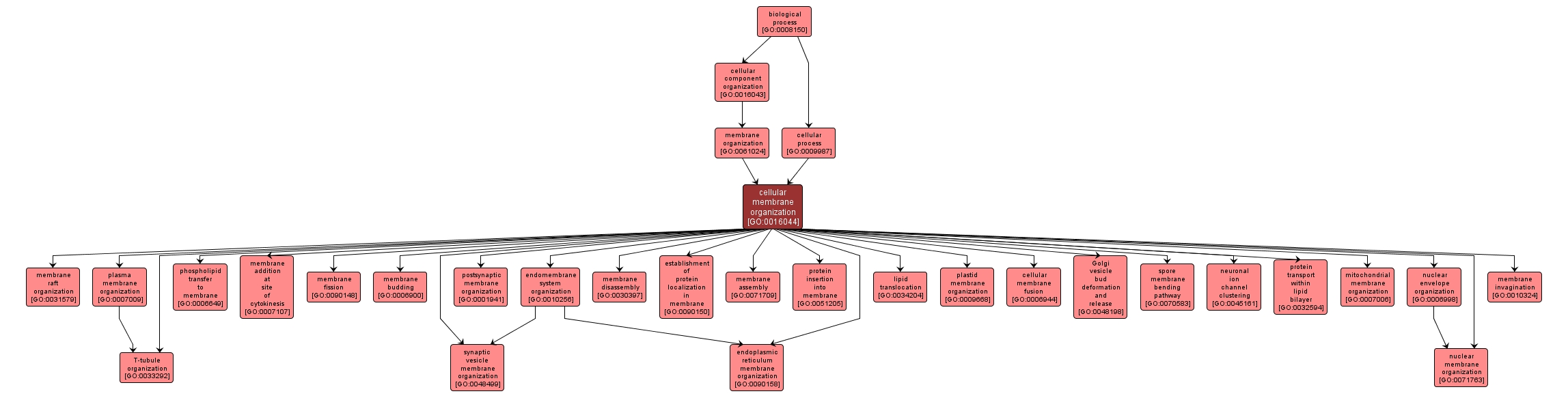
| Desc: |
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of a membrane. A membrane is a double layer of lipid molecules that encloses all cells, and, in eukaryotes, many organelles; may be a single or double lipid bilayer; also includes associated proteins. |