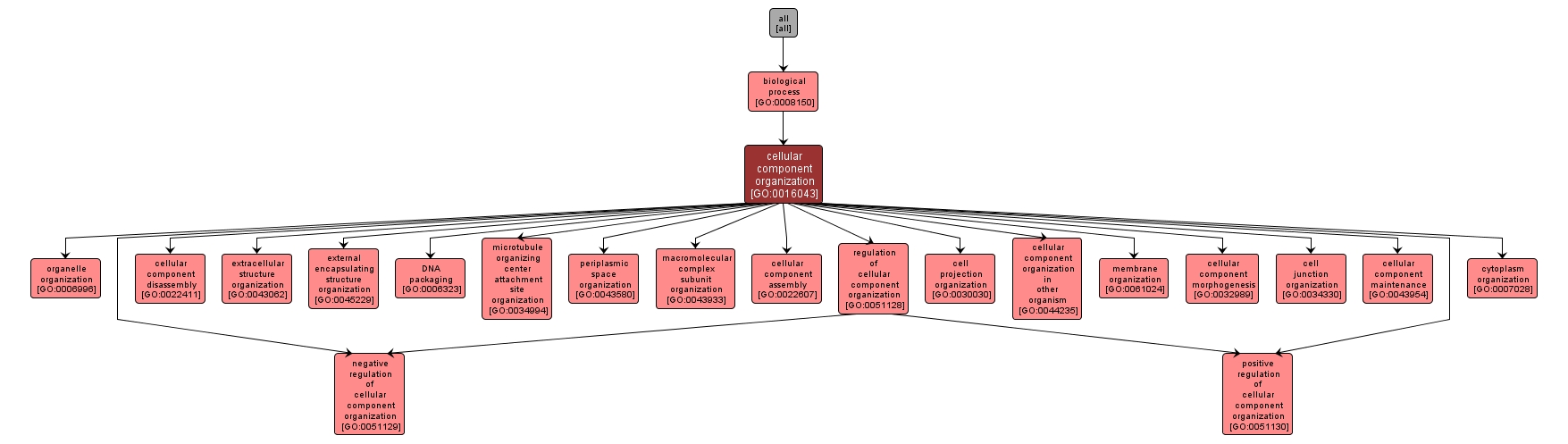
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
cellular component organization |
| Acc: |
GO:0016043 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of a cellular component. |
Synonyms:
- cell organization and biogenesis
- cell organisation
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|