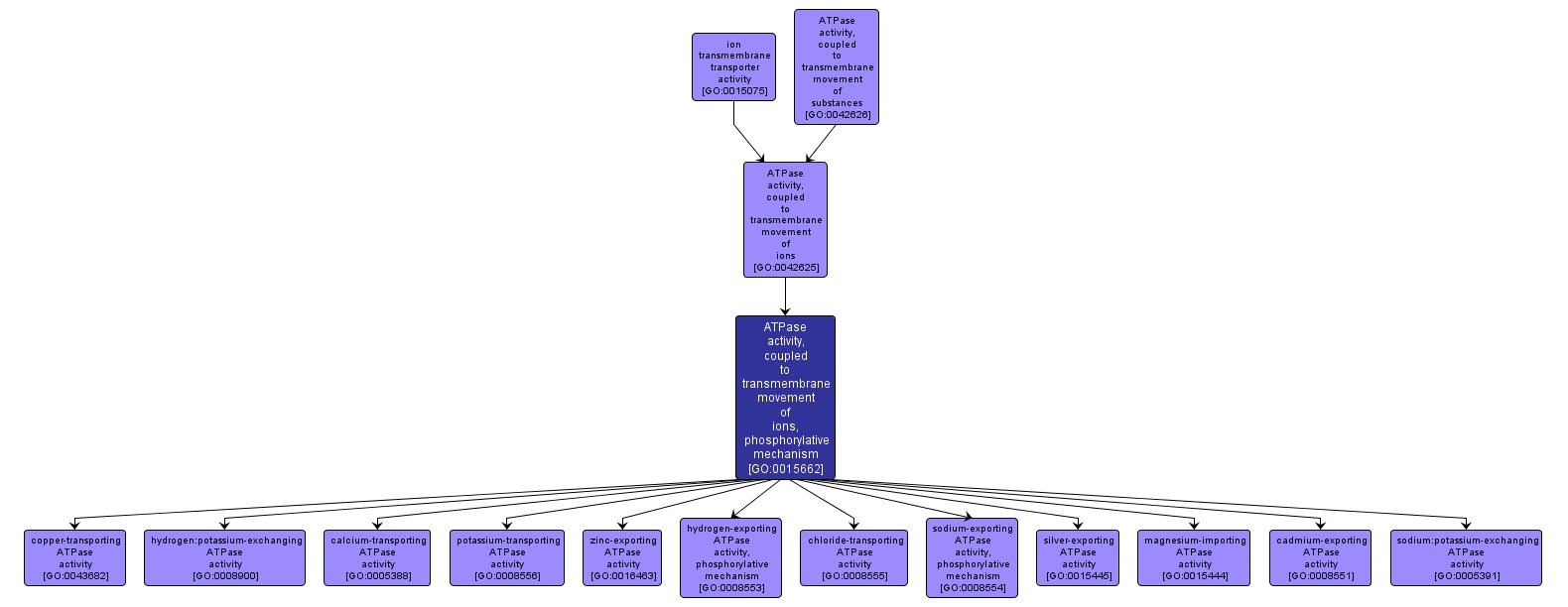
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
ATPase activity, coupled to transmembrane movement of ions, phosphorylative mechanism |
| Acc: |
GO:0015662 |
| Aspect: |
Molecular Function |
| Desc: |
Catalysis of the transfer of a solute or solutes from one side of a membrane to the other according to the reaction: ATP + H2O = ADP + phosphate, to directly drive the transport of ions across a membrane. The reaction is characterized by the transient formation of a high-energy aspartyl-phosphoryl-enzyme intermediate. |
Synonyms:
- zinc, cadmium, cobalt, nickel, lead-efflux ATPase activity
- P-type ATPase activity
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|