| Desc: |
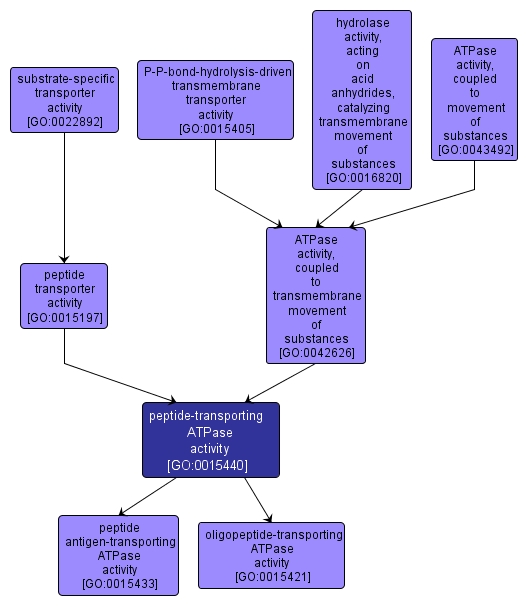
Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + H2O + peptide(in) = ADP + phosphate + peptide(out). Peptides exported include alpha-hemolysin, cyclolysin, colicin V and siderophores from Gram-negative bacteria, and bacteriocin, subtilin, competence factor and pediocin from Gram-positive bacteria. |