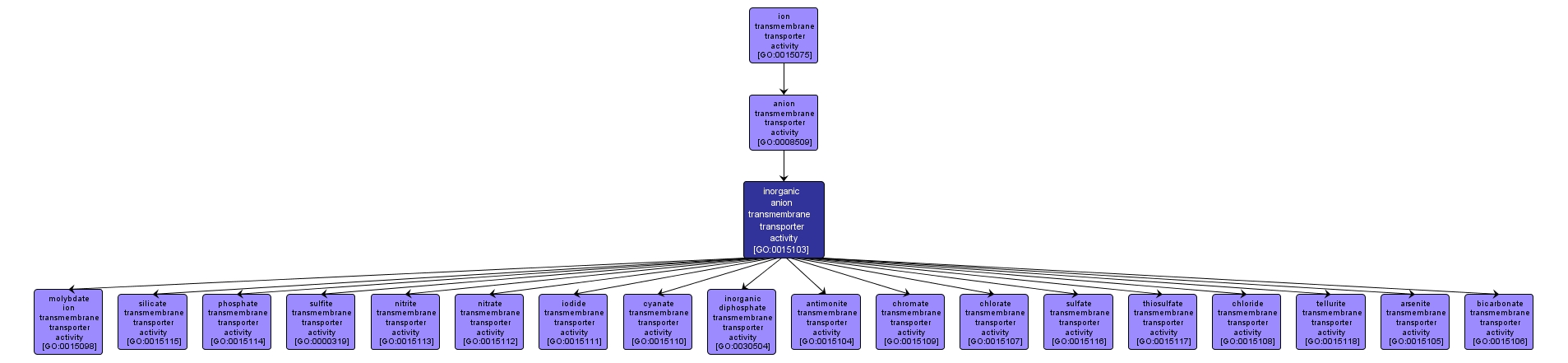
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
inorganic anion transmembrane transporter activity |
| Acc: |
GO:0015103 |
| Aspect: |
Molecular Function |
| Desc: |
Catalysis of the transfer of inorganic anions from one side of a membrane to the other. Inorganic anions are atoms or small molecules with a negative charge which do not contain carbon in covalent linkage. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|