GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
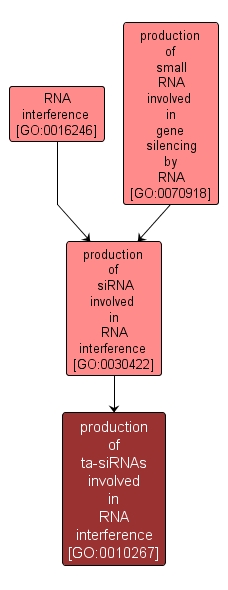
production of ta-siRNAs involved in RNA interference |
| Acc: |
GO:0010267 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
Cleavage of double-stranded RNA to form trans-acting small interfering RNA molecules (siRNAs) of 21-23 nucleotides. ta-siRNAs arise from PolII genes and function like miRNAs to guide cleavage of target mRNAs. |
Synonyms:
- RNA interference, production of ta-siRNAs
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|