GO TERM SUMMARY
|
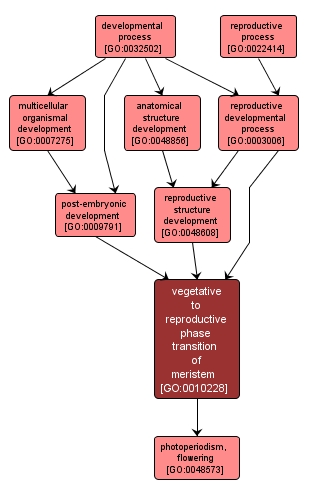
| Name: |
vegetative to reproductive phase transition of meristem |
| Acc: |
GO:0010228 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The process involved in transforming a meristem that produces vegetative structures, such as leaves, into a meristem that produces reproductive structures, such as a flower or an inflorescence. |
Synonyms:
- floral evocation
- transition from vegetative to reproductive phase
- flowering
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|