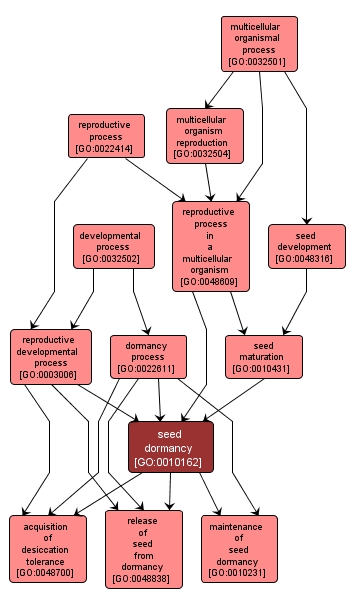
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
seed dormancy |
| Acc: |
GO:0010162 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The process by which a dormant state is induced, maintained and broken in a seed. Dormancy is characterized by a suspension of physiological activity that can be reactivated. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|