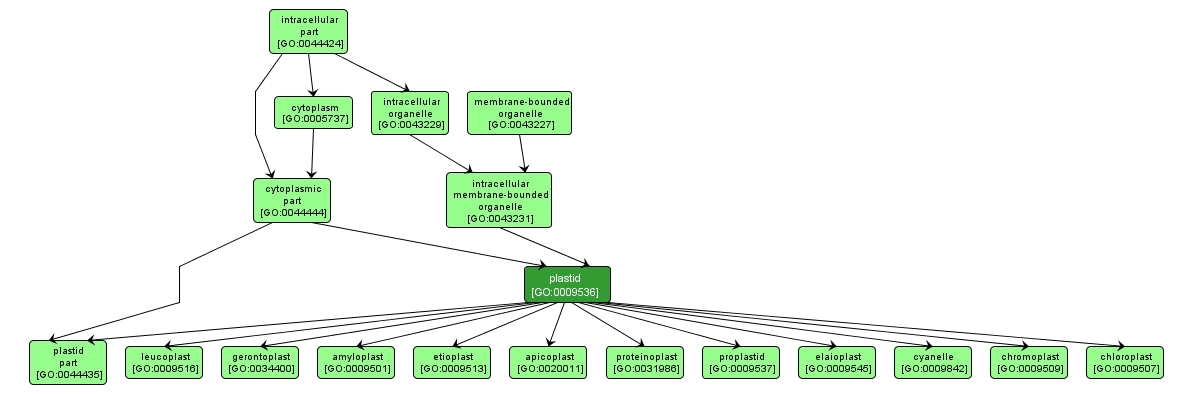
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
plastid |
| Acc: |
GO:0009536 |
| Aspect: |
Cellular Component |
| Desc: |
Any member of a family of organelles found in the cytoplasm of plants and some protists, which are membrane-bounded and contain DNA. Plant plastids develop from a common type, the proplastid. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|