GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
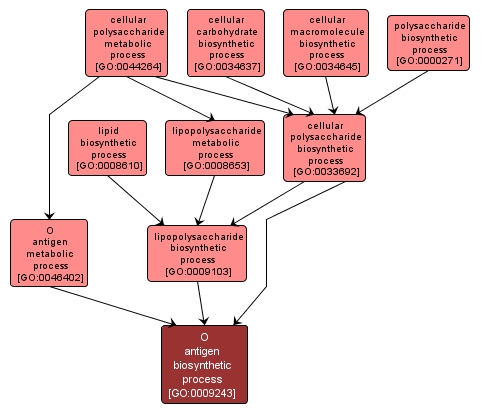
O antigen biosynthetic process |
| Acc: |
GO:0009243 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of the O side chain of a lipopolysaccharide, which determines the antigenic specificity of the organism. It is made up of about 50 repeating units of a branched tetrasaccharide. |
Synonyms:
- O antigen anabolism
- O antigen biosynthesis
- O antigen formation
- O antigen synthesis
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|