| Desc: |
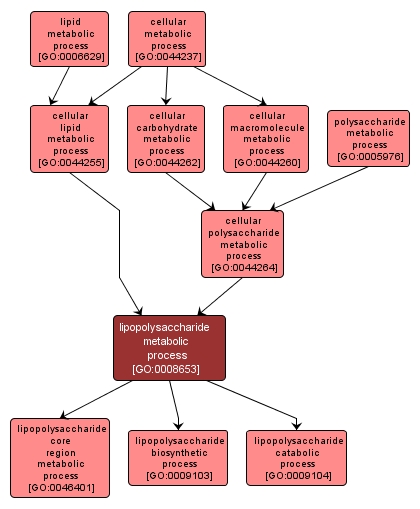
The chemical reactions and pathways involving lipopolysaccharides, any of a group of related, structurally complex components of the outer membrane of Gram-negative bacteria. Lipopolysaccharides consist three covalently linked regions, lipid A, core oligosaccharide, and an O side chain. Lipid A is responsible for the toxicity of the lipopolysaccharide. |