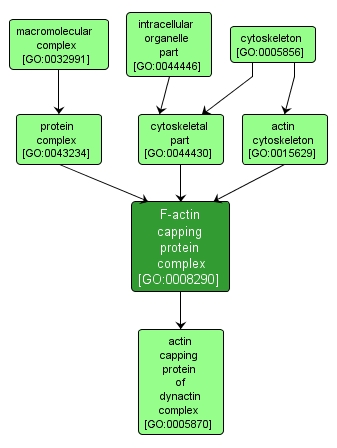
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
F-actin capping protein complex |
| Acc: |
GO:0008290 |
| Aspect: |
Cellular Component |
| Desc: |
A heterodimer consisting of alpha and beta subunits that binds to and caps the barbed ends of actin filaments, thereby regulating the polymerization of actin monomers but not severing actin filaments. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|