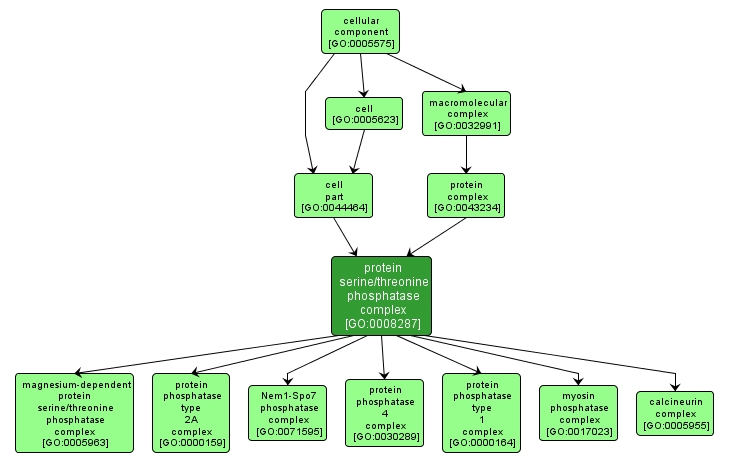
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
protein serine/threonine phosphatase complex |
| Acc: |
GO:0008287 |
| Aspect: |
Cellular Component |
| Desc: |
A complex, normally consisting of a catalytic and a regulatory subunit, which catalyzes the removal of a phosphate group from a serine or threonine residue of a protein. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|