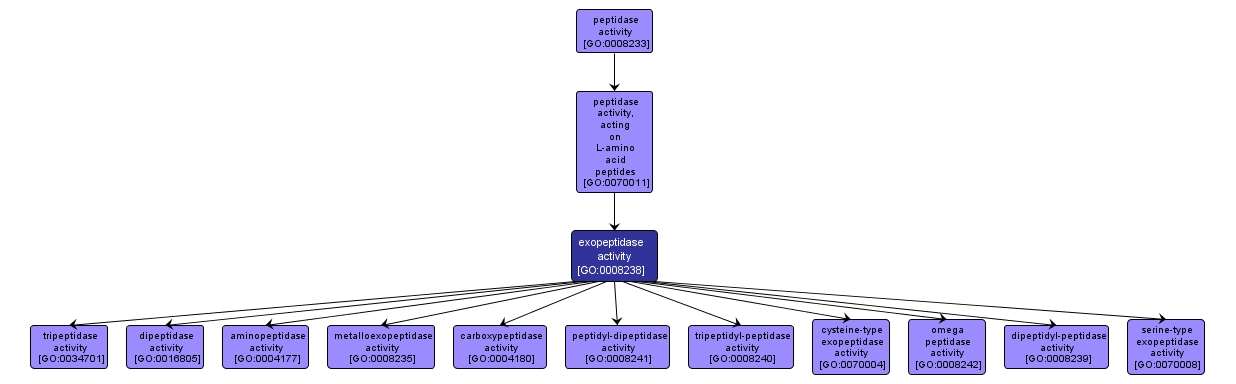
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
exopeptidase activity |
| Acc: |
GO:0008238 |
| Aspect: |
Molecular Function |
| Desc: |
Catalysis of the hydrolysis of a peptide bond not more than three residues from the N- or C-terminus of a polypeptide chain, in a reaction that requires a free N-terminal amino group, C-terminal carboxyl group or both. |
| Synonyms:
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|