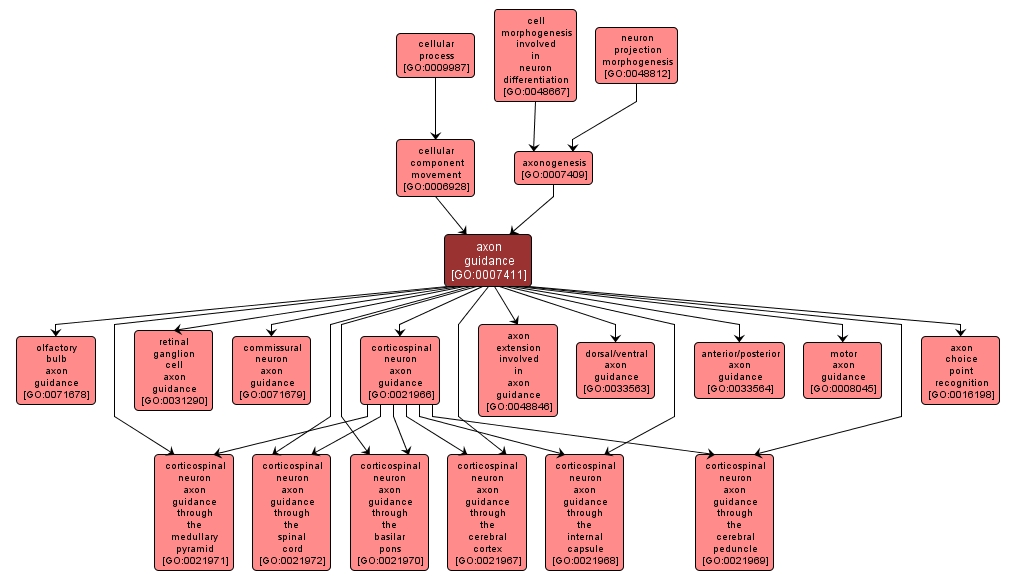
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
axon guidance |
| Acc: |
GO:0007411 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The process by which the migration of an axon growth cone is directed to a specific target site in response to a combination of attractive and repulsive cues. |
Synonyms:
- GO:0008040
- axon pathfinding
- axon growth cone guidance
- axon chemotaxis
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|