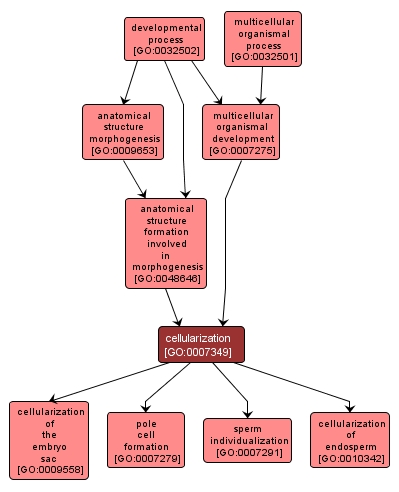
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
cellularization |
| Acc: |
GO:0007349 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The separation of a multi-nucleate cell or syncytium into individual cells. An example of this is found in Drosophila melanogaster embryo development. |
| Synonyms:
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|