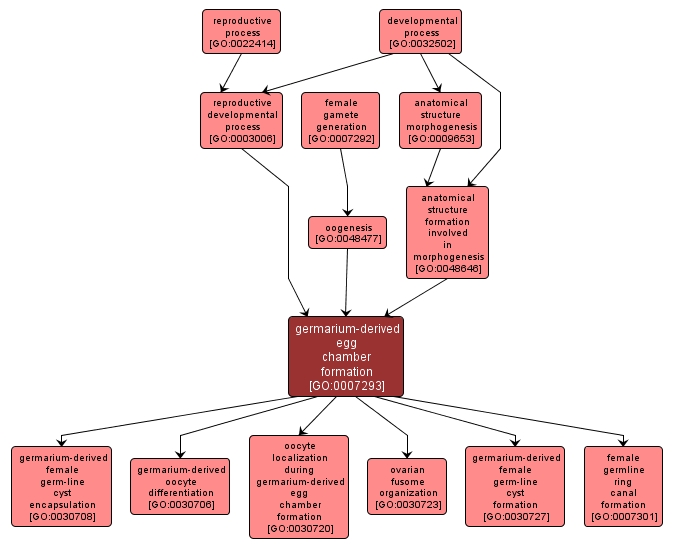
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
germarium-derived egg chamber formation |
| Acc: |
GO:0007293 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
Construction of a stage-1 egg chamber in the anterior part of the germarium, from the progeny of germ-line and somatic stem cells. An example of this is found in Drosophila melanogaster. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|