| Desc: |
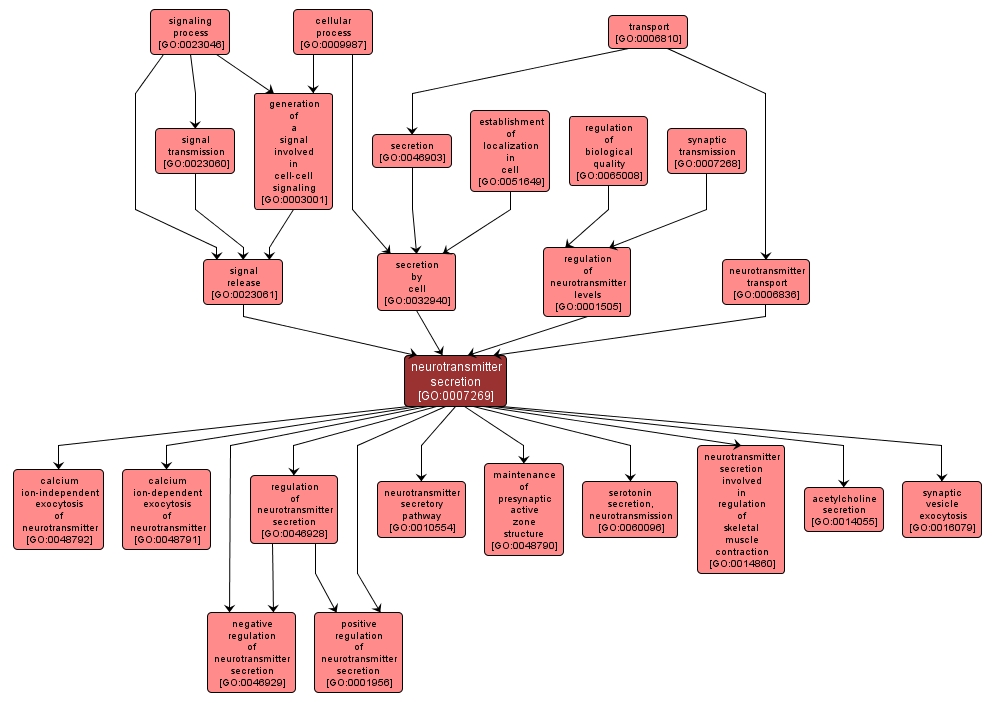
The regulated release of neurotransmitter into the synaptic cleft. A neurotransmitter is any of a group of substances that are released on excitation from the axon terminal of a presynaptic neuron of the central or peripheral nervous system and travel across the synaptic cleft to either excite or inhibit the target cell. Among the many substances that have the properties of a neurotransmitter are acetylcholine, noradrenaline, adrenaline, dopamine, glycine, gamma-aminobutyrate, glutamic acid, substance P, enkephalins, endorphins and serotonin. |