GO TERM SUMMARY
|
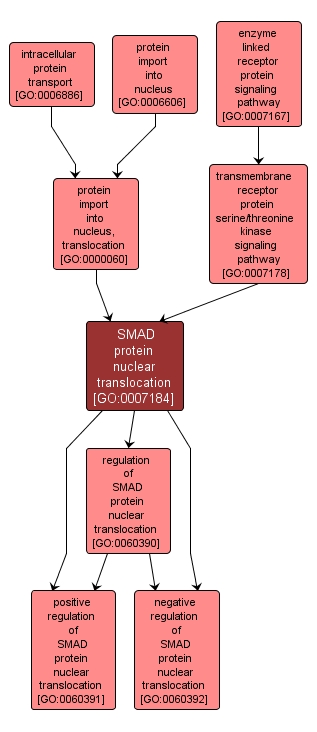
| Name: |
SMAD protein nuclear translocation |
| Acc: |
GO:0007184 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The vectorial transfer of a SMAD proteins from the cytoplasm into the nucleus, through the nuclear pore. Pathway-restricted SMAD proteins and common-partner SMAD proteins are involved in the transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathways. |
Synonyms:
- SMAD protein import into nucleus, translocation
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|