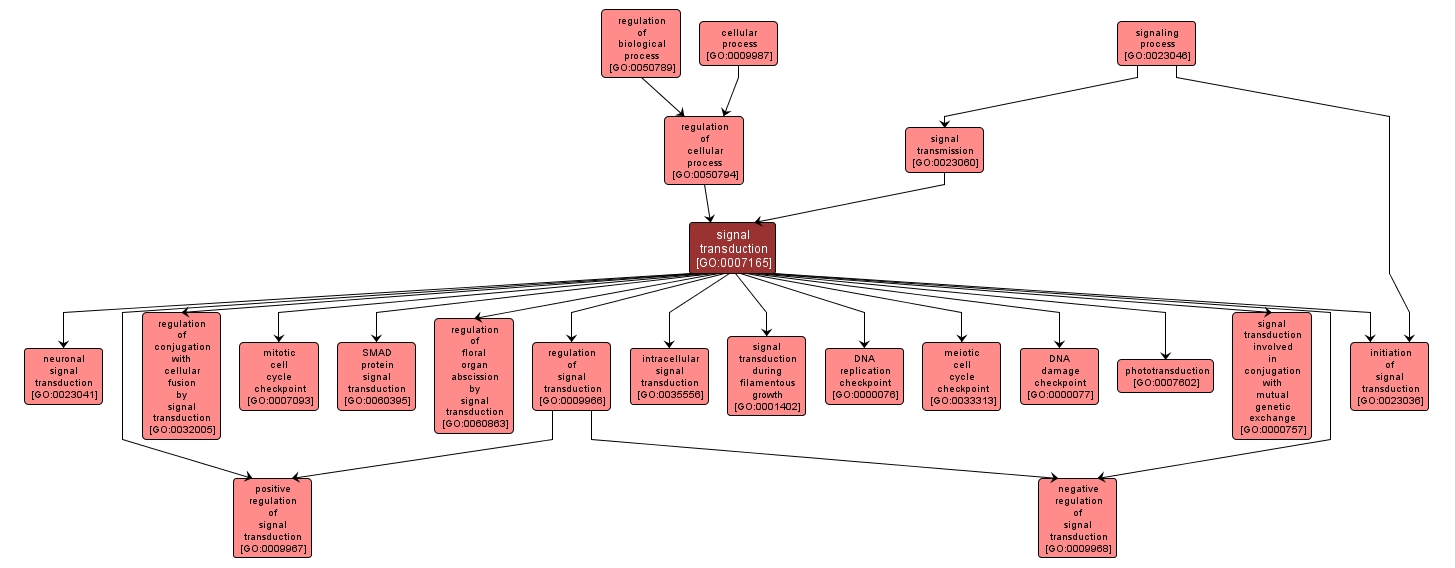
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
signal transduction |
| Acc: |
GO:0007165 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The process whereby an activated receptor conveys information down the signaling pathway, resulting in a change in the function or state of a cell. |
Synonyms:
- signaling cascade
- signalling cascade
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|