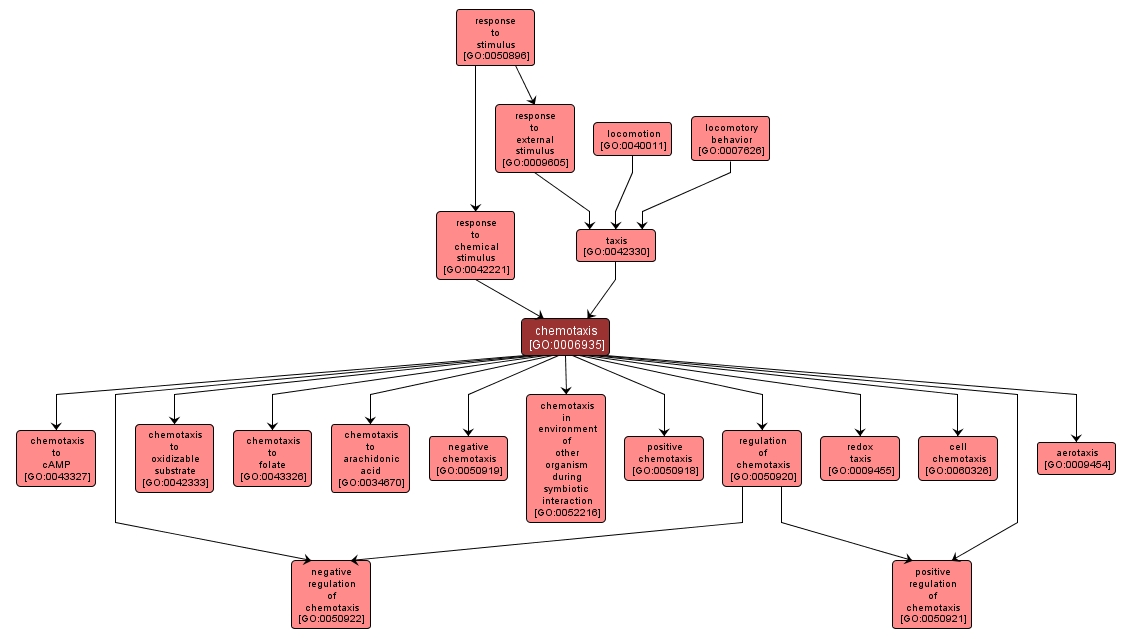
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
chemotaxis |
| Acc: |
GO:0006935 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The directed movement of a motile cell or organism, or the directed growth of a cell guided by a specific chemical concentration gradient. Movement may be towards a higher concentration (positive chemotaxis) or towards a lower concentration (negative chemotaxis). |
Synonyms:
- taxis in response to chemical stimulus
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|