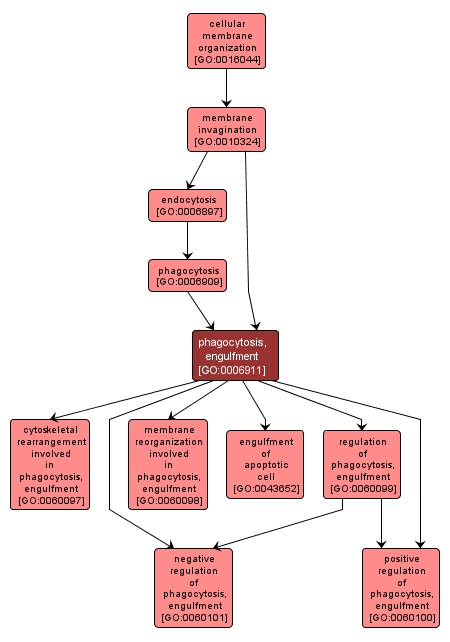
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
phagocytosis, engulfment |
| Acc: |
GO:0006911 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The internalization of bacteria, immune complexes and other particulate matter or of an apoptotic cell by phagocytosis, including the membrane and cytoskeletal processes required, which involves one of three mechanisms: zippering of pseudopods around a target via repeated receptor-ligand interactions, sinking of the target directly into plasma membrane of the phagocytosing cell, or induced uptake via an enhanced membrane ruffling of the phagocytosing cell similar to macropinocytosis. |
Synonyms:
- phagosome formation
- phagosome biosynthesis
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|