GO TERM SUMMARY
|
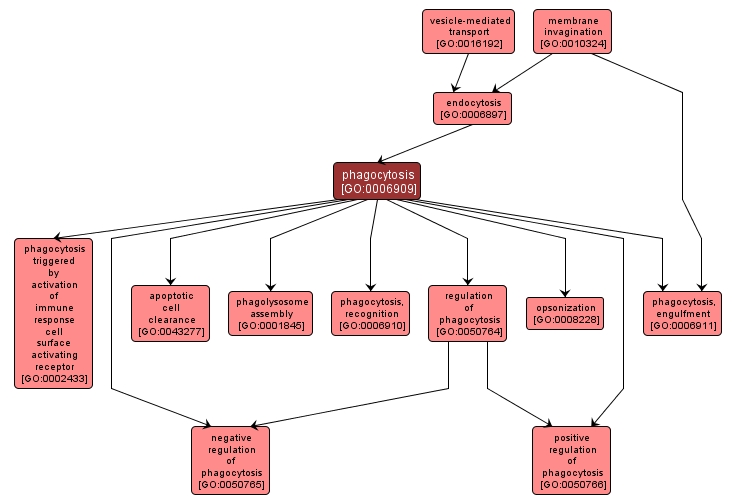
| Name: |
phagocytosis |
| Acc: |
GO:0006909 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The process whereby phagocytes engulf external particulate material. The particles are initially contained within phagocytic vacuoles (phagosomes), which then fuse with primary lysosomes to effect digestion of the particles. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|