| Desc: |
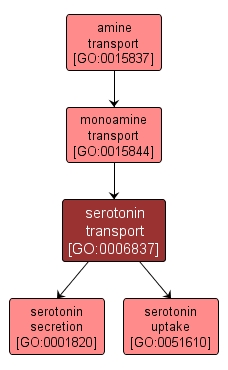
The directed movement of serotonin into, out of, within or between cells by means of some external agent such as a transporter or pore. Serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine) is a monoamine neurotransmitter occurring in the peripheral and central nervous systems. |