| Desc: |
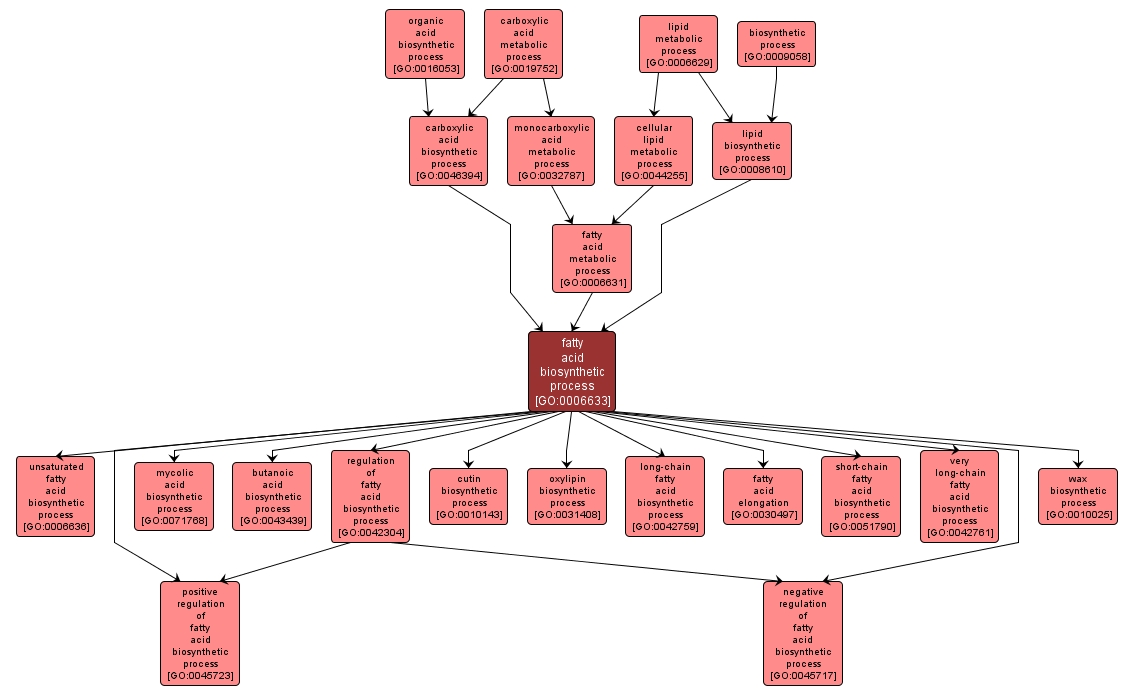
The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of a fatty acid, any of the aliphatic monocarboxylic acids that can be liberated by hydrolysis from naturally occurring fats and oils. Fatty acids are predominantly straight-chain acids of 4 to 24 carbon atoms, which may be saturated or unsaturated; branched fatty acids and hydroxy fatty acids also occur, and very long chain acids of over 30 carbons are found in waxes. |