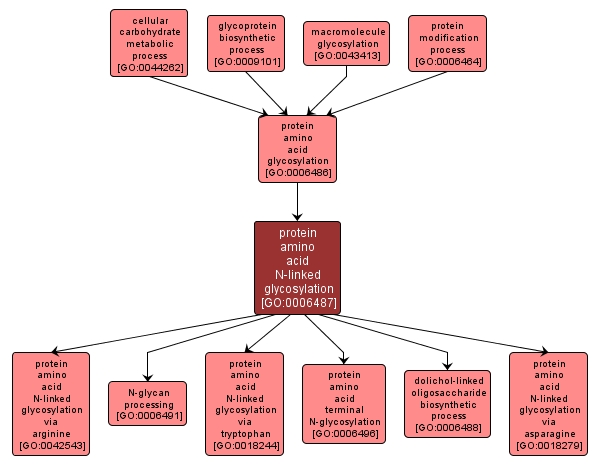
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
protein amino acid N-linked glycosylation |
| Acc: |
GO:0006487 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
A protein amino acid glycosylation process in which a sugar unit is added to a protein via the N4 atom of peptidyl-asparagine, the omega-N of arginine, or the N1' atom peptidyl-tryptophan. |
Synonyms:
- N-glycan metabolism
- N-glycan biosynthesis
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|