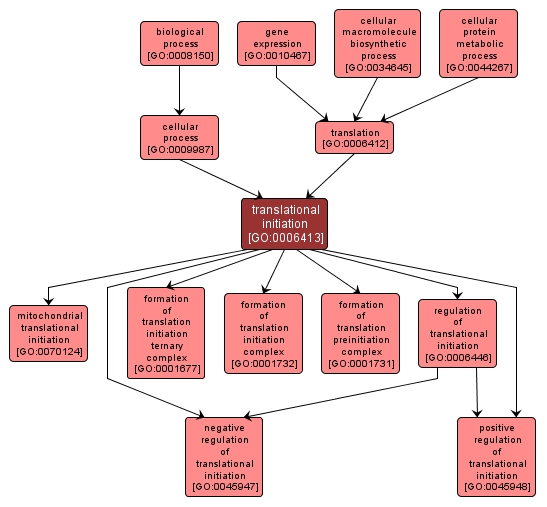
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
translational initiation |
| Acc: |
GO:0006413 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The process preceding formation of the peptide bond between the first two amino acids of a protein. This includes the formation of a complex of the ribosome, mRNA, and an initiation complex that contains the first aminoacyl-tRNA. |
Synonyms:
- biopolymerisation
- biopolymerization
- protein synthesis initiation
- translation initiation
- GO:0006454
- GO:0006440
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|