GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
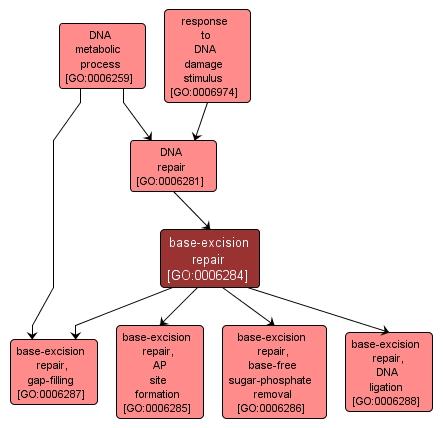
base-excision repair |
| Acc: |
GO:0006284 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
In base excision repair, an altered base is removed by a DNA glycosylase enzyme, followed by excision of the resulting sugar phosphate. The small gap left in the DNA helix is filled in by the sequential action of DNA polymerase and DNA ligase. |
| Synonyms:
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|