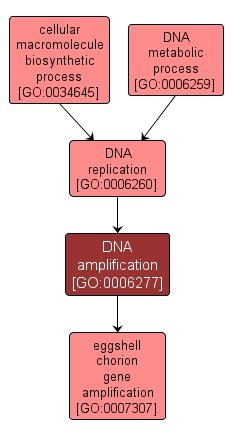
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
DNA amplification |
| Acc: |
GO:0006277 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The process by which the number of copies of a gene is increased in certain cells as extra copies of DNA are made in response to certain signals of cell development or of stress from the environment. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|