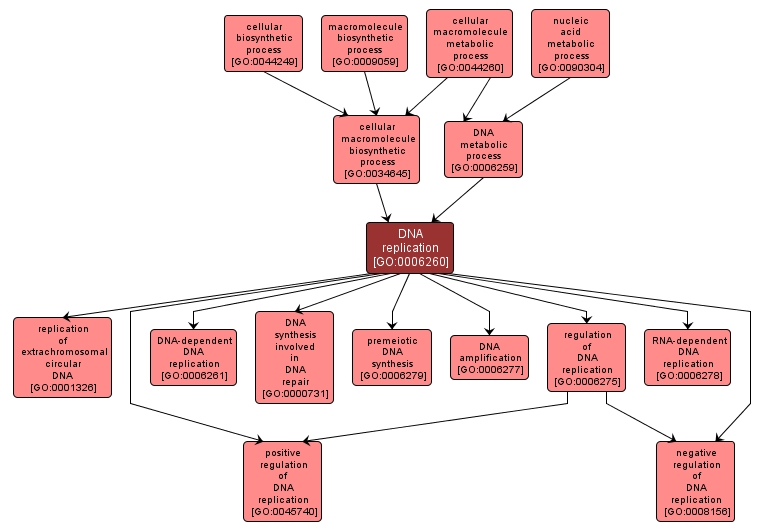
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
DNA replication |
| Acc: |
GO:0006260 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The cellular metabolic process whereby new strands of DNA are synthesized. The template for replication can either be an existing DNA molecule or RNA. |
Synonyms:
- DNA biosynthesis
- DNA biosynthetic process
- GO:0055133
- DNA synthesis
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|