GO TERM SUMMARY
|
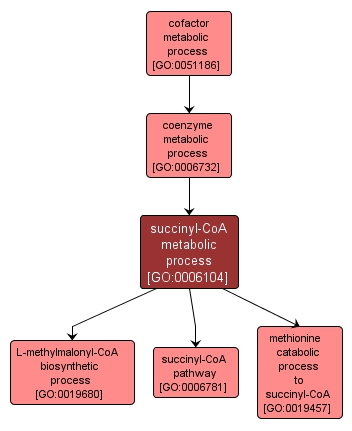
| Name: |
succinyl-CoA metabolic process |
| Acc: |
GO:0006104 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The chemical reactions and pathways involving succinyl-CoA, a compound composed of the monovalent acyl group 3-carboxypropanoyl, derived from succinic acid by loss of one OH group, linked to coenzyme A. |
| Synonyms:
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|