| Desc: |
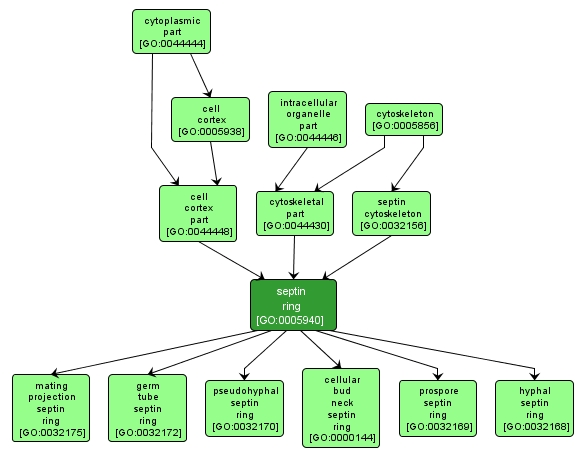
A tight ring-shaped structure that forms in the division plane at the site of cytokinesis; composed of members of the conserved family of filament-forming proteins called septins as well as septin-associated proteins. This type of septin structure is observed at the bud neck of budding fungal cells, at the site of cell division in animal cells, at the junction between the mother cell and a pseudohyphal projection, and also within hyphae of filamentous fungi at sites where a septum will form. |