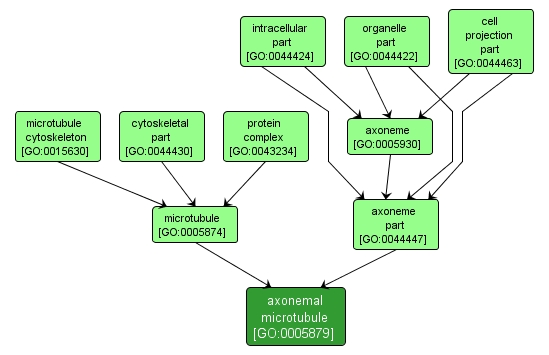
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
axonemal microtubule |
| Acc: |
GO:0005879 |
| Aspect: |
Cellular Component |
| Desc: |
A microtubule in the axoneme of a cilium or flagellum; an axoneme contains nine modified doublet microtubules surrounding a pair of single microtubules. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|