GO TERM SUMMARY
|
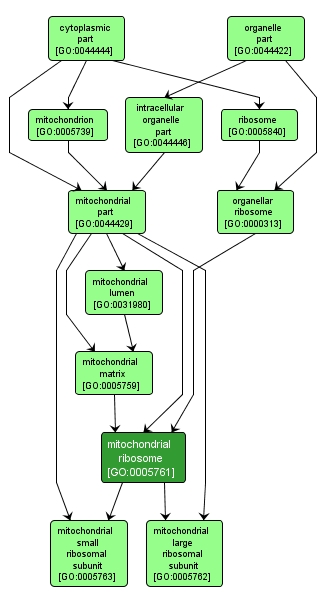
| Name: |
mitochondrial ribosome |
| Acc: |
GO:0005761 |
| Aspect: |
Cellular Component |
| Desc: |
A ribosome found in the mitochondrion of a eukaryotic cell; contains a characteristic set of proteins distinct from those of cytosolic ribosomes. |
Synonyms:
- 55S ribosome, mitochondrial
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|