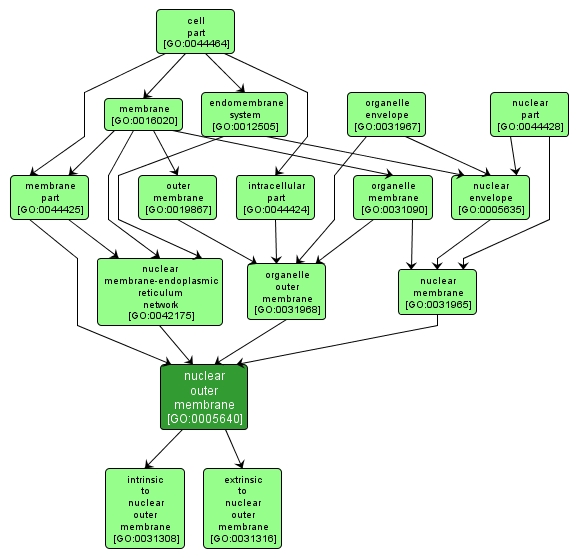
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
nuclear outer membrane |
| Acc: |
GO:0005640 |
| Aspect: |
Cellular Component |
| Desc: |
The outer, i.e. cytoplasm-facing, lipid bilayer of the nuclear envelope; continuous with the endoplasmic reticulum of the cell and sometimes studded with ribosomes. |
Synonyms:
- perinuclear membrane
- outer envelope
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|