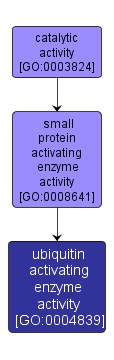
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
ubiquitin activating enzyme activity |
| Acc: |
GO:0004839 |
| Aspect: |
Molecular Function |
| Desc: |
Catalysis of the activation of the C-terminal carboxyl group of ubiquitin by the formation of a high-energy thiolester bond in an ATP-dependent manner. |
| Synonyms:
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|