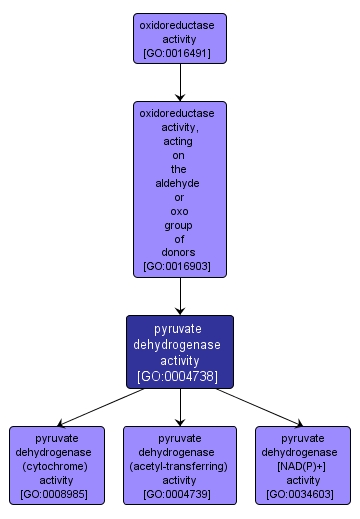
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
pyruvate dehydrogenase activity |
| Acc: |
GO:0004738 |
| Aspect: |
Molecular Function |
| Desc: |
Catalysis of the oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate. |
Synonyms:
- pyruvic dehydrogenase activity
- pyruvic acid dehydrogenase activity
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|