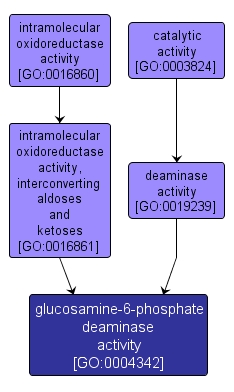
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
glucosamine-6-phosphate deaminase activity |
| Acc: |
GO:0004342 |
| Aspect: |
Molecular Function |
| Desc: |
Catalysis of the reaction: D-glucosamine 6-phosphate + H2O = D-fructose 6-phosphate + NH3. |
Synonyms:
- glucosamine phosphate deaminase activity
- phosphoglucosamine isomerase activity
- phosphoglucosaminisomerase activity
- GlcN6P deaminase activity
- 2-amino-2-deoxy-D-glucose-6-phosphate aminohydrolase (ketol isomerizing)
- aminodeoxyglucosephosphate isomerase activity
- glucosamine-6-phosphate isomerase activity
- glucosaminephosphate isomerase
|