GO TERM SUMMARY
|
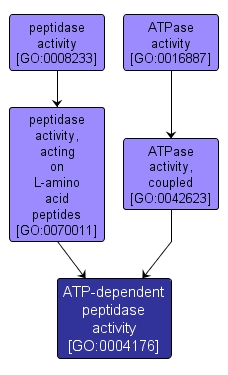
| Name: |
ATP-dependent peptidase activity |
| Acc: |
GO:0004176 |
| Aspect: |
Molecular Function |
| Desc: |
Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + H2O = ADP + phosphate to drive the hydrolysis of peptide bonds. |
Synonyms:
- GO:0004280
- ATP-dependent proteolysis
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|