GO TERM SUMMARY
|
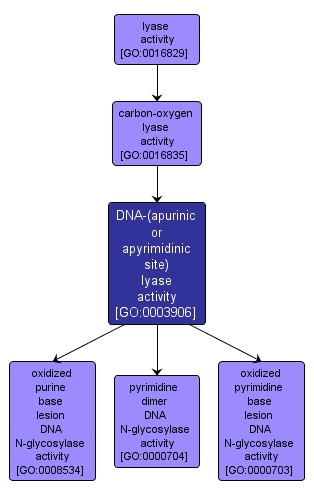
| Name: |
DNA-(apurinic or apyrimidinic site) lyase activity |
| Acc: |
GO:0003906 |
| Aspect: |
Molecular Function |
| Desc: |
Catalysis of the cleavage of the C-O-P bond 3' to the apurinic or apyrimidinic site in DNA by a beta-elimination reaction, leaving a 3'-terminal unsaturated sugar and a product with a terminal 5'-phosphate. |
Synonyms:
- Phage-T4 UV endonuclease activity
- Micrococcus luteus UV endonuclease activity
- endodeoxyribonuclease (apurinic or apyrimidinic) activity
- phage-T4 UV endonuclease
- AP endonuclease class I activity
- X-ray endonuclease III
- Phage-T(4) UV endonuclease activity
- AP site-DNA 5'-phosphomonoester-lyase activity
- deoxyribonuclease (apurinic or apyrimidinic) activity
- endonuclease VIII activity
- E. coli endonuclease III
- DNA-(apurinic or apyrimidinic site) 5'-phosphomonoester-lyase activity
- micrococcus luteus UV endonuclease
- AP lyase activity
- E. coli endonuclease III activity
|