GO TERM SUMMARY
|
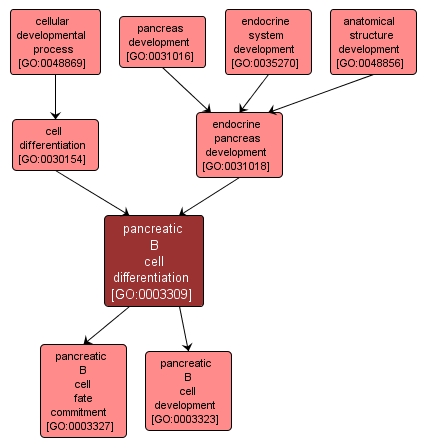
| Name: |
pancreatic B cell differentiation |
| Acc: |
GO:0003309 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The process whereby relatively unspecialized cells acquire specialized structural and/or functional features of a pancreatic beta cell. Beta cells are cells of the pancreas that secrete insulin. |
Synonyms:
- pancreatic beta cell differentiation
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|