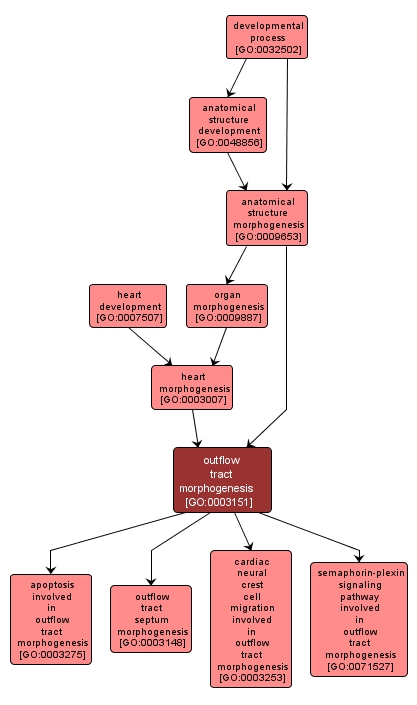
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
outflow tract morphogenesis |
| Acc: |
GO:0003151 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The process by which the anatomical structures of the outflow tract are generated and organized. Morphogenesis pertains to the creation of form. The outflow tract is the portion of the heart through which blood flows into the arteries. |
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|