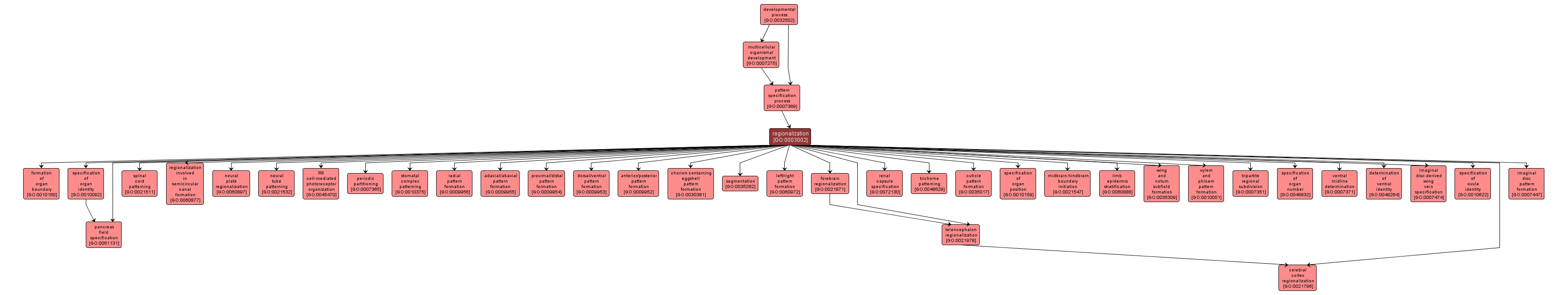
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
regionalization |
| Acc: |
GO:0003002 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The pattern specification process by which an axis or axes is subdivided in space to define an area or volume in which specific patterns of cell differentiation will take place or in which cells interpret a specific environment. |
| Synonyms:
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|