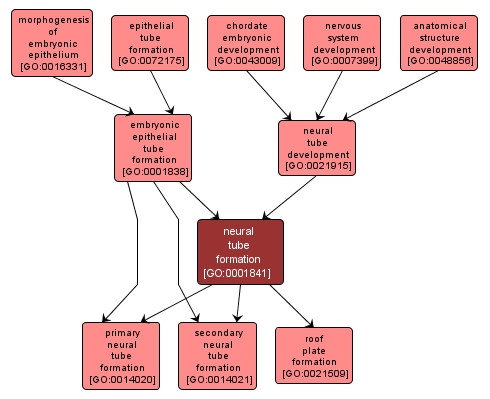
GO TERM SUMMARY
|
| Name: |
neural tube formation |
| Acc: |
GO:0001841 |
| Aspect: |
Biological Process |
| Desc: |
The formation of a tube from the flat layer of ectodermal cells known as the neural plate. This will give rise to the central nervous system. |
Synonyms:
- GO:0001679
- neurulation
- neural tube morphogenesis
|
|

|
INTERACTIVE GO GRAPH
|